- 主机及实例IP
- Slave的配置参数
- 配置主从同步
- 配置SSH免秘钥,四台服务器之间可互通
- 四个节点安装EPEL源以及相关yum包
- 下载安装mha包
- 建立与授权mha用户
- manager节点建立相关目录和配置文件
- 相关配置文件内容
- 主库启动一个虚IP
- 失败切换脚本
- 手动在线切换脚本
- failover后发送邮件脚本
- 修改脚本属主属组,并且增加执行权限
- 检查SSH的配置
- 检查MHA的配置
- 启动MHA的服务
- 发生failover主从切换后,MHAmanager服务会自动停掉,且在manager_workdir目录下面生成文件app1.failover.complete,若想要启动MHA,必须先确保没有此文件
- 在线手动切换主从,如果MHA在运行,需要先停止MHA,然后再检查MHA当前设置
- 手动切换
- 注意
目录
Master High Availability又称MHA,是一套优秀的作为MySQL高可用性环境下故障切换和主从提升的软件。MySQL故障切换过程中,MHA能够做到在30秒之内自动完成数据库的故障切换操作,并在进行故障切换的过程中,MHA能在最大程度上保证数据的一致性,以达到真正意义上的高可用。
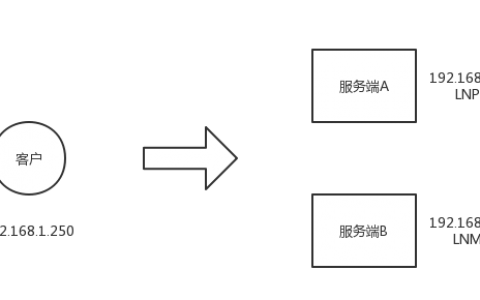
主机及实例IP
- Manager : 192.168.18.250
- Master : 172.16.18.2:3306
- Slave1 : 172.16.18.3:3306
- Slave2 : 172.16.18.4:3306
- VIP : 172.16.18.5
Slave的配置参数
- log_bin=/home/birdteam/log/mysql-bin
- read_only=1
- relay_log_purge=0
- #一主一从不用此项,两从及以上建议打开此参数,防止切换为成主库的从库自动删除中继日志后,无法给其他从库应用这部分日志
配置主从同步
- mysql>grant replication slave on *.* to ‘repl_17zuoye’@’%’ identified by ‘office.repl.17zuoye’;
- mysql>flush privileges;
- #三个节点都要配置,用于当某个slave升为主后其他的从进行同步
- mysql>change master to master_host=’172.16.18.2‘,master_user=’dtstack’,master_port=3306,master_password=’abc123′,master_log_file=’logbin.000014‘,master_log_pos=70980879;
- mysql>start slave;
配置SSH免秘钥,四台服务器之间可互通
- # ssh-keygen -t rsa
- # ssh-copy-id -i .ssh/id_rsa.pub root@172.16.18.2
四个节点安装EPEL源以及相关yum包
- # rpm -ivh http://download.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/6/x86_64/epel-release-6-8.noarch.rpm
- # yum -y install perl-DBD-MySQL perl-Config-Tiny perl-Log-Dispatch perl-Parallel-ForkManager perlTime-HiRes
下载安装mha包
- # wget https://code.google.com/p/mysql-master-ha/wiki/Downloads?tm=2
- manager节点:
- # rpm –ivh mha4mysql-manager-0.56–0.el6.noarch.rpm
- # rpm –ivh mha4mysql-node-0.56–0.el6.noarch.rpm
- node 节点:
- # rpm –ivh mha4mysql-node-0.56–0.el6.noarch.rpm
建立与授权mha用户
- mysql>GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON *.* TO ‘mha’@’%’ IDENTIFIED BY ‘mhamha’;
- mysql>flush privileges;
manager节点建立相关目录和配置文件
- # tree /mha
- /mha
- ├── app1
- │ ├── app1.conf
- │ └── manager.log
- └── conf
- ├── master_ip_failover_3306
- ├── master_ip_online_change
- └── send_report
- 2 directories, 5 files
相关配置文件内容
- # cat app1.conf
- [server default]
- manager_workdir = /mha/app1
- manager_log = /mha/app1/manager.log
- remote_workdir = /mha/app1
- master_ip_failover_script=/mha/conf/master_ip_failover_3306
- #master failover时执行
- report_script=/mha/conf/send_report
- #master failover时执行,发送邮件使用
- master_ip_online_change_script=/mha/conf/master_ip_online_change
- #master_switchover时执行(手动切换)
- user=mha
- password=mhamha
- ping_interval=1
- ping_type=CONNECT
- repl_password=office.repl.17zuoye
- repl_user=repl_17zuoye
- ssh_port=22
- ssh_user=root
- [server1]
- hostname = 10.200.3.2
- port=3306
- master_binlog_dir = /database1/data_5.6.17_3306/binlog
- candidate_master = 1
- #这个服务器有较高的优先级提升为新的master(还要具备:开启binlog使复制没有延迟)
- [server2]
- hostname = 10.200.3.3
- port=3306
- master_binlog_dir = /database1/data_5.6.17_3306/binlog
- candidate_master =1
- ignore_fail=1
- [server3]
- hostname = 10.200.3.4
- port=3306
- master_binlog_dir = /database1/data_5.6.17_3306/binlog
- candidate_master =1
- ignore_fail=1
- #如slave存在故障,在主库出现问题时默认情况下mha不会进行故障切换,该参数即设定MHA会在所有的机器有问题的时间也会进行故障切换
- no_master=1
- #不将这台主机转换为master
主库启动一个虚IP
- # /sbin/ifconfig em1:0 10.200.3.5/23 up
失败切换脚本
- # cat master_ip_failover_3306
- #!/usr/bin/env perl
- use strict;
- use warnings FATAL => ‘all’;
- use Getopt::Long;
- my (
- $command, $ssh_user, $orig_master_host, $orig_master_ip,
- $orig_master_port, $new_master_host, $new_master_ip, $new_master_port
- );
- my $vip = ‘10.200.3.5/23‘; # Virtual IP
- my $key = “0”;
- my $ssh_start_vip = “/sbin/ifconfig em1:$key $vip”;
- my $start_new_master_vip = “/sbin/ifconfig em1:$key $vip”;
- my $ssh_stop_vip = “/sbin/ifconfig em1:$key down”;
- my $arp = “/usr/sbin/arping -A -q -c 2 -I em1:$key 10.200.3.5”;
- #虚IP配置,在哪个网卡上,key编号的对应
- GetOptions(
- ‘command=s’ => \$command,
- ‘ssh_user=s’ => \$ssh_user,
- ‘orig_master_host=s’ => \$orig_master_host,
- ‘orig_master_ip=s’ => \$orig_master_ip,
- ‘orig_master_port=i’ => \$orig_master_port,
- ‘new_master_host=s’ => \$new_master_host,
- ‘new_master_ip=s’ => \$new_master_ip,
- ‘new_master_port=i’ => \$new_master_port,
- );
- exit &main();
- sub main {
- print “\n\nIN SCRIPT TEST====$ssh_stop_vip==$start_new_master_vip===\n\n”;
- if ( $command eq “stop” || $command eq “stopssh” ) {
- # $orig_master_host, $orig_master_ip, $orig_master_port are passed.
- # If you manage master ip address at global catalog database,
- # invalidate orig_master_ip here.
- my $exit_code = 1;
- eval {
- print “Disabling the VIP on old master: $orig_master_host \n”;
- &stop_vip();
- $exit_code = 0;
- };
- if ($@) {
- warn “Got Error: $@\n”;
- exit $exit_code;
- }
- exit $exit_code;
- }
- elsif ( $command eq “start” ) {
- # all arguments are passed.
- # If you manage master ip address at global catalog database,
- # activate new_master_ip here.
- # You can also grant write access (create user, set read_only=0, etc) here.
- my $exit_code = 10;
- eval {
- print “Enabling the VIP – $vip on the new master – $new_master_host \n”;
- &start_vip();
- $exit_code = 0;
- };
- if ($@) {
- warn $@;
- exit $exit_code;
- }
- exit $exit_code;
- }
- elsif ( $command eq “status” ) {
- # print “Checking the Status of the script.. OK \n”;
- # `ssh $ssh_user\@tm01.okooo.cn \” $ssh_start_vip \”`;
- exit 0;
- }
- else {
- &usage();
- exit 1;
- }
- }
- # A simple system call that enable the VIP on the new master
- sub start_vip() {
- `ssh root\@$new_master_host \” $ssh_start_vip \”`;
- `ssh root\@$new_master_host \” $arp \”`;
- }
- # A simple system call that disable the VIP on the old_master
- sub stop_vip() {
- return 0 unless ($ssh_user);
- `ssh $ssh_user\@$orig_master_host \” $ssh_stop_vip \”`;
- }
- sub usage {
- “Usage: master_ip_failover –command=start|stop|stopssh|status –orig_master_host=host –orig_master_ip=ip –orig_master_port=port –new_master_host=host –new_master_ip=ip –new_master_port=port\n”;
- }
手动在线切换脚本
- # cat master_ip_online_change
- #!/usr/bin/env perl
- use strict;
- use warnings FATAL =>’all’;
- use Getopt::Long;
- my $vip = ‘10.200.3.5/23‘; # Virtual IP
- my $key = “0”;
- my $ssh_start_vip = “/sbin/ifconfig em1:$key $vip”;
- my $ssh_stop_vip = “/sbin/ifconfig em1:$key down”;
- my $exit_code = 0;
- my (
- $command, $orig_master_is_new_slave, $orig_master_host,
- $orig_master_ip, $orig_master_port, $orig_master_user,
- $orig_master_password, $orig_master_ssh_user, $new_master_host,
- $new_master_ip, $new_master_port, $new_master_user,
- $new_master_password, $new_master_ssh_user,
- );
- GetOptions(
- ‘command=s’ => \$command,
- ‘orig_master_is_new_slave’ => \$orig_master_is_new_slave,
- ‘orig_master_host=s’ => \$orig_master_host,
- ‘orig_master_ip=s’ => \$orig_master_ip,
- ‘orig_master_port=i’ => \$orig_master_port,
- ‘orig_master_user=s’ => \$orig_master_user,
- ‘orig_master_password=s’ => \$orig_master_password,
- ‘orig_master_ssh_user=s’ => \$orig_master_ssh_user,
- ‘new_master_host=s’ => \$new_master_host,
- ‘new_master_ip=s’ => \$new_master_ip,
- ‘new_master_port=i’ => \$new_master_port,
- ‘new_master_user=s’ => \$new_master_user,
- ‘new_master_password=s’ => \$new_master_password,
- ‘new_master_ssh_user=s’ => \$new_master_ssh_user,
- );
- exit &main();
- sub main {
- #print “\n\nIN SCRIPT TEST====$ssh_stop_vip==$ssh_start_vip===\n\n”;
- if ( $command eq “stop” || $command eq “stopssh” ) {
- # $orig_master_host, $orig_master_ip, $orig_master_port are passed.
- # If you manage master ip address at global catalog database,
- # invalidate orig_master_ip here.
- my $exit_code = 1;
- eval {
- print “\n\n\n***************************************************************\n”;
- print “Disabling the VIP – $vip on old master: $orig_master_host\n”;
- print “***************************************************************\n\n\n\n”;
- &stop_vip();
- $exit_code = 0;
- };
- if ($@) {
- warn “Got Error: $@\n”;
- exit $exit_code;
- }
- exit $exit_code;
- }
- elsif ( $command eq “start” ) {
- # all arguments are passed.
- # If you manage master ip address at global catalog database,
- # activate new_master_ip here.
- # You can also grant write access (create user, set read_only=0, etc) here.
- my $exit_code = 10;
- eval {
- print “\n\n\n***************************************************************\n”;
- print “Enabling the VIP – $vip on new master: $new_master_host \n”;
- print “***************************************************************\n\n\n\n”;
- &start_vip();
- $exit_code = 0;
- };
- if ($@) {
- warn $@;
- exit $exit_code;
- }
- exit $exit_code;
- }
- elsif ( $command eq “status” ) {
- print “Checking the Status of the script.. OK \n”;
- `ssh $orig_master_ssh_user\@$orig_master_host \” $ssh_start_vip \”`;
- exit 0;
- }
- else {
- &usage();
- exit 1;
- }
- }
- # A simple system call that enable the VIP on the new master
- sub start_vip() {
- `ssh $new_master_ssh_user\@$new_master_host \” $ssh_start_vip \”`;
- }
- # A simple system call that disable the VIP on the old_master
- sub stop_vip() {
- `ssh $orig_master_ssh_user\@$orig_master_host \” $ssh_stop_vip \”`;
- }
- sub usage {
- “Usage: master_ip_failover –command=start|stop|stopssh|status –orig_master_host=host –orig_master_ip=ip –orig_master_port=po
- rt –new_master_host=host –new_master_ip=ip –new_master_port=port\n”;
- }
failover后发送邮件脚本
- # cat send_report
- #!/bin/bash
- source /root/.bash_profile
- orig_master_host=`echo “$1” | awk -F = ‘{print $2}’`
- new_master_host=`echo “$2” | awk -F = ‘{print $2}’`
- new_slave_hosts=`echo “$3” | awk -F = ‘{print $2}’`
- subject=`echo “$4” | awk -F = ‘{print $2}’`
- body=`echo “$5” | awk -F = ‘{print $2}’`
- #判断日志结尾是否有successfully,有则表示切换成功,成功与否都发邮件
- tac /mha/app1/manager.log | sed -n 2p | grep ‘successfully’ > /dev/null
- if [ $? -eq 0 ]
- then
- echo -e “MHA $subject 主从切换成功\n master:$orig_master_host –> $new_master_host \n $body \n 当前从库:$new_slave_hosts” | mailx -s “MySQL实例宕掉,MHA $subject 切换成功” noreply@birdteam.net
- else
- echo -e “MHA $subject 主从切换失败\n master:$orig_master_host –> $new_master_host \n $body” | mailx -s “MySQL实例宕掉,MHA $subject 切换失败” noreply@birdteam.net
- fi
修改脚本属主属组,并且增加执行权限
- # chown mysql.mysql ./*
- # chmod +x ./*
检查SSH的配置
- # masterha_check_ssh –conf=/mha/app1/app1.conf
- Tue Jan 5 17:16:41 2016 – [info] All SSH connectiontests passed successfully.
检查MHA的配置
- # masterha_check_repl –conf=/mha/app1/app1.conf
- MySQL Replication Health is OK.
启动MHA的服务
- # masterha_manager –conf=/mha/app1/app1.conf
发生failover主从切换后,MHAmanager服务会自动停掉,且在manager_workdir目录下面生成文件app1.failover.complete,若想要启动MHA,必须先确保没有此文件
- # ll
- total 80
- -rw-r–r– 1 mysql mysql 556 Aug 29 11:23 app1.conf
- -rw-r–r– 1 root root 0 Aug 29 15:33 app1.failover.complete
- -rw-r–r– 1 root root 69838 Aug 29 15:33 manager.log
- -rw-r–r– 1 root root 143 Aug 29 15:33 saved_master_binlog_from_192.168.100.111_3306_20160829153340.binlog
在线手动切换主从,如果MHA在运行,需要先停止MHA,然后再检查MHA当前设置
- # masterha_check_repl –conf=/mha/app1/app1.conf
手动切换
- 如果不指定new_master_host,则会根据配置文件app1.cnf选出new_master_host,但new_master_port默认是3306
- masterha_master_switch –master_state=alive –conf=/mha/app1/app1.conf –orig_master_is_new_slave -running_updates_limit=3600 –interactive=0
- 以下为切换时指定了new_master_host和new_master_port
- masterha_master_switch –master_state=alive –conf=/mha/app1/app1.conf –orig_master_is_new_slave -running_updates_limit=3600 –interactive=0 –new_master_host=10.200.3.2 –new_master_port=3306
- 参数–running_updates_limit如果现在master执行写操作的执行时间大于这个参数,或任何一台slave的Seconds_Behind_Master大于这个参数,那么master switch将自动放弃,默认参数为1s;
- 参数–interactive=0非交互切换,建议加上,可以大大加快切换速度,加上后库不忙时大概3秒内切换完成。
注意
- 如果需要将现有的从库修改为从,再启动mha的时候可能会报错;
- Wed Sep 7 12:18:56 2016 – [error][/usr/share/perl5/vendor_perl/MHA/ServerManager.pm, ln671] Master 192.168.100.111:3306 from which slave 10.200.3.2(10.200.3.2:3306) replicates is not defined in the configuration file!
- 切换脚本可在MHA的官网查看。
www.ysidc.top 西数超哥博客,数据库,西数超哥,虚拟主机,域名注册,域名,云服务器,云主机,云建站,ysidc.top